Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease. It manifests itself in the form of skin rashes. The initial phase is characterized by symptoms similar to the clinical picture of other pathologies of the epidermis. To prevent the progression of the disease, to facilitate its course, it is necessary to differentiate the pathology. To do this, you need to know the symptoms, manifestations of psoriasis at different stages.
Causes in adults and children
Why psoriasis occurs in children and adults, medical scientists have yet to find out precisely. There is only speculation about the cause of the development of this disease. Therefore, it is assumed that psoriasis can be inherited: in people whose parents suffered from this skin disease, psoriatic rash is often seen. Some doctors associate the development of the pathology with immune instability, metabolic disorders and the presence of a chronic infection. In most patients, doctors observe severe hyperlipidemia.
To check susceptibility to such a disease, you need to perform a classic genome analysis. Those with ten chromosomal loci are more likely to develop psoriasis. The main genome responsible for congenital predisposition is PSORS1.
Psoriasis can develop at any age: in children, young people, the elderly. In adults, according to medical scientists, the following factors cause the disease:
- low immunity;
- chronic fatigue;
- alcohol abuse;
- severe stress;
- poor hygiene;
- constant excesses;
- insect bite;
- infectious pathologies (influenza, ARVI); vaccination
- ;
- temperature difference; vitamin deficiency;
- smoking;
- long-term medicine;
- burn;
- allergy;
- hormonal imbalance;
- climate change;
- inadequate nutrition.
Children experience psoriatic rashes more often:
- after sore throat;
- if there is a chronic infection in the body;
- with low immunity.
Psoriasis should not be started:People with this diagnosis increase the risk of early atherosclerotic vascular lesions and the occurrence of cardiac pathologies. There is also the threat of arthritis.
Most of the time, psoriasis occurs in people with low heredity.
How psoriasis manifests

Psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of large plaques on the skin. The spots are initially insignificant and appear on the parts of the body where the skin is thicker (on the elbows, knees). These formations flake off. When scratching, sores appear, which turn pale in the morning.
The disease is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Stearin staining.These are small scaly papules fused into plaques.
- Terminal film.Under the psoriatic plaques, there is a thin, shiny pink skin. Your doctor can see after removing all the scales.
- Identify bleeding(blood dew syndrome). If the terminal film is damaged as a result of scraping the stratum corneum of the epidermis, drops of blood will appear.
These manifestations together are called the psoriatic triad. They are detected during a sample of the inflamed area of the skin.
Psoriasis also has the following symptoms:
- the formation of new papules in case of skin lesion and enlargement of the lesion area; The
- elements of the eruption have a dense structure;
- there is a red border around the board;
- weakness;
- the presence of a whitish 3 mm pseudo-atrophic border around the rash;
- purulent skin odor (when pustules form);
- the phenomenon of oily formation, in which a yellowish-brown spot appears under the nail plate;
- proliferative acanthosis, in which the skin becomes thicker, the interpapillary processes lengthen;
- thimble symptom (nail psoriasis); scabies.
As psoriasis is a chronic condition, its symptoms begin to disappear after a while, the wounds heal. But then the papules form again.
The first symptoms of the onset of the disease
In the first stage of psoriasis, a rash always forms on the skin.
At the beginning, it is almost invisible, without characteristic scales. Several points of rash appear on the limbs.
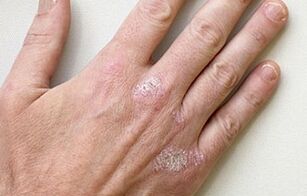
After a few weeks, the number of affected areas increases. The rash melts into large plates, which are covered with silver scales. The itching in the early stages of psoriasis is moderate. The person complains of chronic fatigue, weakness.
These symptoms are also characteristic of allergic skin reactions, dermatitis and herpes zoster. Therefore, it is important to make the differential diagnosis.
On examination, the doctor discovers the psoriatic triad. By the size of the rash, the doctor determines the etiology of psoriasis: drop-shaped, dotted or coin-shaped.
Signs of a progressive stage of the disease
As the disease progresses, the number of papules increases and the rash spreads to healthy areas of the body. The slightest scratch, swelling, or burn will cause a nodular skin rash. The second stage takes a long time. On palpation, you can find dense boundaries between the inflamed areas of the epidermis. The plates have a border that stands out for its bright color and is covered by scales.
In the last stage of the disease, the symptoms gradually begin to disappear. The plates become lighter, their edges fade. After a while, the papules disappear, in their place is dry skin, hyperpigmented spots.
The temperature in psoriasis can only increase in the presence of an inflammatory process, acne suppuration. So, the affected areas can hurt.
What is the stearic spot phenomenon
Stearin stains are the main symptom that forms the psoriatic triad. It is a small area with papular elements of the eruption, which are strongly scaly. The more the doctor shaves the affected skin, the more the peeling appears. During manipulation, the person does not feel pain. The phenomenon got its name because the detachable scales on the skin look like stearin patches.
Where it appears first of all: rash location
At first, psoriatic rashes form on the elbows, feet and knees. Then, the papules spread to areas of the body with thinner and more delicate skin: on the lower leg, lower back, wrist, abdomen, groin area, scalp. The rash can be located elsewhere. But these areas of the body are most affected by psoriasis.
In the absence of proper treatment, the disease spreads to the nails, mucous membranes and joints.
The location of the psoriatic rash in adults can be:
- Head. Rashes are seen on the scalp, ears, occiput, eyebrows, eyelids, eyes, nasolabial folds.
- Lower limbs.
- Elbows. Scaly plaques are formed that become rough over time.
- Upper limbs. A small rash similar to hives occurs.
In children, rashes usually appear at:
- legs;
- buttocks;
- skin folds;
- elbows;
- the scalp.
How scaly scalp starts on the head
Scaly lichen can spread throughout the body. It is usually acute. A rash turns from a pearl to a pea. The wheal is covered with silver and white scales. The rashes increase in size over time, they merge into a single focus with uneven edges. This board has a clear border. When psoriasis affects the scalp, a psoriatic crown forms: red pustules with purulent content appear behind the ears and along the forehead line.
How quickly the pathology develops
How quickly psoriasis develops depends on its shape. Therefore, the type of pathology in the form of a drop is distinguished by the ability to appear and disappear abruptly. Severe plaque psoriasis is characterized by the gradual spread of pustules throughout the body. The rash is then covered with flaking scales in a short period. Skin rashes coalesce to form large plaques.
Diagnostic methods
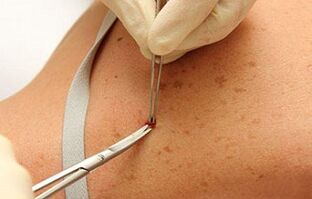
If psoriasis is suspected, consult a dermatologist. The doctor makes a presumptive diagnosis based on the patient's complaints and examination. The doctor gives referrals to do laboratory, instrumental research. Differential diagnoses are also performed.
When the disease progresses, it is recommended to donate blood for analysis to detect an acute, autoimmune or rheumatic process. In severe situations, a biopsy is also performed, which shows the accumulation of Rete bodies, thickening of the layer, infiltration of the skin by polybasts, T lymphocytes, dendritic cells, increased angiogenesis under psoriatic plaques.
For differential diagnosis, run:
- allergy test
- ; serum biochemical test
- ;
- stool analysis for dysbiosis;
- histological biopsy examination.
No special tests are needed to diagnose psoriasis in children. The pathology is detected based on the examination of the elements of the rash.
How to treat psoriasis
As psoriasis is considered a chronic condition, it cannot be completely cured. The goal of therapy is to achieve stable remission and eliminate complications. To do this, use drugs, physical therapy, popular methods. In severe cases, the patient is hospitalized. In the initial stage, therapy can be performed at home.
Therapy in the clinic
To treat psoriatic lesions, doctors prescribe antihistamines to relieve swelling, itching and redness.

Enzymatic agents are also used. They stimulate the body to produce the necessary enzymes. Damage to the skin of the body causes discomfort, stiffness.
The perception that a disease cannot be cured causes psychological problems. Therefore, doctors prescribe sedative medications to help restore the emotional state.
Hepatoprotectors are used to improve liver function. Inflammation and itching can be relieved with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To strengthen the body, immunomodulators are prescribed.
Physiotherapy techniques are also used. They help to remove pigmentation and speed healing. Doctors recommend:
- selective phytotherapy;
- laser action on the skin;
- ultrasound treatment;
- magnetotherapy.
In a hospital, the patient is under constant supervision by doctors. Therefore, it is easy to track the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment regimen, to make timely adjustments to the applied therapy.
Home treatment
After hospital discharge, treatment continues. To maintain normal health, to achieve a stable remission, doctors prescribe several drugs in one course. Complexes of vitamins, ointments and folk remedies are used.
The patient should treat the skin areas affected by psoriasis daily with hormonal and non-hormonal ointments.
To improve the condition of the epidermis, dermatologists prescribe vitamins. Vitamins A, E, D and C are especially useful in the fight against psoriasis. They strengthen the body's defenses, help restore and cleanse the skin.

Traditional healers suggest the use of activated charcoal. One of the main reasons for the development of psoriasis are metabolic disorders, intoxication. Activated carbon acts as an absorbent, so it cleans the body of harmful substances well. It should be consumed for one month, twice a day, in the dosage of 1 tablet per kilogram of body weight.
White clay helps to restore the skin. Relieves inflammation, dries and removes itching. Baths with the addition of sea salt are also useful.
When treating psoriasis at home, it is recommended to adhere to a number of rules:
- Take medicines prescribed by the doctor in the indicated dose.
- Treat the skin with ointments and creams.
- Remove the scabs carefully after softening.
- Soak up the air and sun.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Observe the daily routine, diet.
- Get enough rest.
- Take breaks while taking the medication.
By adhering to these recommendations, a person can prevent a relapse of the disease.
Therefore, psoriasis is a serious chronic disease. The reasons for its development have not been precisely established, only the provocative factors are known. The disease has characteristic symptoms, but in the first stage it is similar to other skin pathologies. To identify and start treating the disease in time, you need to contact a dermatologist when a suspected rash appears.























